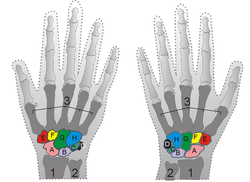
The lunate bone (semilunar bone) is a bone in the human hand that may be distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row of the carpus, or wrist, between the scaphoid and triangular bone.
The etymology derives from the Latin luna which means "moon."
See also
Bone terminology
Terms for anatomical location


No comments:
Post a Comment