
Otto Wallach (27 March 1847 at Königsberg - 26 February 1931 at Göttingen) was a Jewish German chemist who won the Nobel Prize in 1910 for work on alicyclic compounds.
Biography
During his work with Friedrich Kekulé in Bonn he started a systematic analysis of the terpenes present in essential oils. Up to this time the only few were isolated in pure form and the structural information were sparse. Melting point comparison and the measurement of mixtures was one of the methods to confirm identical substances. For this method the mostly liquid terpenes had to be transformed into crystalline compounds. With stepwise derivatisation especially additions to the double bond present in some of the terpenes he achieved the goal to obtain crystalline compounds. The investigation of the rearrangement reactions of cyclic unsaturated terpenes made it possible to optain the structure of a unknown terpene by following the rearangments to a known structure of a terpene. With these principal methods he opened the path to a systematical rearch on terpenes.
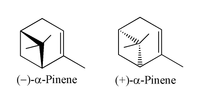
He was responsible for naming the terpene, pinene, and for undertaking the first systematic study of pinene^ . He also proposed that terpenes can be regarded as oligomers of isoprene; this is now known as the isoprene rule, and it assisted in the elucidation of the structures of many terpenes.
He wrote a book about the chemistry of Terpenes, "Terpene und Campher" (1909).


No comments:
Post a Comment